Photo: nature.com
Improved allele frequencies in gnomAD through local ancestry inference - Nature Communications
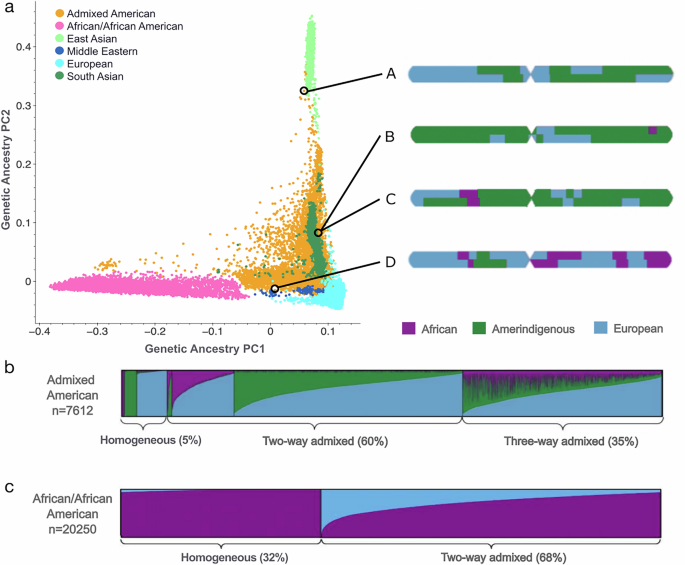
The study in Nature Communications reveals improved allele frequencies in gnomAD through local ancestry inference, enhancing understanding of genetic diversity in populations.
- The research focuses on genetic ancestry analysis, emphasizing that genetic ancestry does not determine individual self-identification, crucial for understanding complex genetic backgrounds.
- Local ancestry inference techniques were applied to gnomAD data, resulting in refined allele frequency estimates that reflect genetic admixture across diverse populations in the United States.
- The study adheres to current nomenclature standards for race and ethnicity in the United States census, ensuring accurate representation of genetic diversity among sampled individuals.
Why It Matters
This research enhances our understanding of genetic diversity, which is vital for personalized medicine and public health initiatives. Populations with complex genetic backgrounds may benefit from more accurate genetic assessments. Future studies might expand on these findings to inform genetic research and healthcare practices.